Maximising the stable environment - covering aspects such as ventilation, flooring, bedding, lighting and the use of therapeutic tools for the stabled horse
/Article by Adam Jackson
Horses stay in their stables for different durations based on their care, training regime, health status, and seasonal changes. Ensuring your horse's comfort and well-being in their stable is crucial, as inadequately designed facilities can lead to injuries, health issues, and fire hazards. With horse welfare under the spotlight with the focus being on the keeping and protection of animals under the European Union review, there is no better time to look at how we can maximise the stable environment.
Ammonia
Ammonia is a serious irritant that can harm the respiratory tract and cause breathing difficulties. Lower concentrations of ammonia can irritate a horse's upper respiratory tract, while higher levels may skip this area and lead to inflammation and fluid buildup in the lower lungs. Ammonia triggers inflammation, which increases mucus production and disrupts the function of cilia in the respiratory tract, negatively impacting the immune response. When cilia malfunction, dust and dirt can accumulate in a horse's lungs, causing health issues and decreased performance.
Monitoring ammonia levels in stables is crucial, as levels should ideally be below 10 ppm, and an odour of ammonia typically indicates levels are dangerously elevated at 20-30 ppm, which can harm horses' health.
Bedding
Ammonia can be managed effectively through proper stable management in addition to ensuring good ventilation. To improve the absorption of urine and faeces and lower ammonia levels, add extra dry bedding in the areas of the stable where the horse often soils. A recent study has shown that even with regular cleaning, elevated ammonia levels can remain near the floors. Using a combination of highly absorbent bedding materials and an ammonia-neutralising product can help lower ammonia levels.
Bedding made of pine shavings is excellent at controlling the ammonia levels. The pine oil in the shavings tends to inhibit the bacteria that converts urine into ammonia, thus keeping the ammonia levels low. In addition, bedding that has strong shavings provide cushioning rather than compacting together.
Stable floor setups
The type of surface on which a horse stands for extended periods can significantly influence its comfort, movement quality, and overall soundness. Consequently, it is essential to invest time and resources in choosing the appropriate flooring for your stables. Moreover, selecting the right flooring can enhance operational efficiency and lower costs associated with hygiene management and stable cleaning. Finally, conduct routine inspections of your flooring to guarantee safety and avert potential hazards.
There are two main categories of flooring: permeable and impermeable.
Permeable or porous stable flooring can consist of either conventional packed clay or a specially engineered geotextile membrane. In the case of the latter, the membrane layers act as a barrier between the horse and bedding and the underlying base material.
In both scenarios, it is essential to install pervious materials on a foundation of well-graded crushed and compacted stone. There are disadvantages associated with the use of pervious flooring. While packed clay is softer than cement or asphalt, it is prone to becoming uneven when exposed to additional moisture, particularly if deep bedding is not utilised.
Membrane layers can also contribute to urine accumulation, leading to an increase in ammonia levels that negatively impact the respiratory health of horses. Furthermore, this moisture can permeate the underlying base material, resulting in the development of unpleasant odours. Another significant issue with this type of stall construction is the potential for groundwater contamination.
Stable flooring that is impermeable or impervious is specifically engineered to stop urine and moisture from seeping through. To facilitate the elimination of urine and faeces, it is essential to either grant the horse access to an outdoor space or to supply bedding that can absorb moisture and offer cushioning.
It is essential to have a solid foundation beneath for the entire system to function effectively. Stall flooring consists of a base layer and an upper layer of material. If the base is not properly established, the overall performance will be compromised.
Additionally, rubber matting is regarded as an ideal durable choice due to its ability to mitigate hardness, alleviate fatigue in the horse's legs, and simplify the cleaning process. Rubber mats may require a significant initial investment; however, they offer long-term benefits by facilitating consistent cleaning, lowering bedding expenses, and enhancing the health, comfort, and overall wellbeing of horses.
A correctly installed rubber mat should be even and stable while offering a degree of cushioning. The market offers a range of matting options, including custom wall-to-wall installations and interlocking mats. It may be beneficial to explore mats that are thicker and more cushioned to provide insulation against cold floors and to minimise the risk of pain in the hip, stifle, hock, fetlock, and pastern areas.
In certain circumstances, it may be necessary to install a drain in a non-porous stall to facilitate the collection of liquids. A drain is particularly beneficial in veterinary or maternity stalls that require regular washing. Drains should be situated near a wall, and the stall should be graded appropriately. If drains are installed, ensure that cleanout traps are included to capture and eliminate solid waste.
Ventilation
Good ventilation in stables is essential for removing bad odours, improving indoor air quality and humidity, which supports horse health, while also controlling temperature and condensation to extend the building's lifespan.
Horses are obligate nasal-breathers and grazing posture hinder their ability to effectively clear dust and debris from their respiratory systems. Prioritising good ventilation is essential for maintaining horses' health, as it mitigates the risks of respiratory diseases caused by airborne pollutants. Failure to minimise airborne particulate matter like mould, mildew, and dust-borne bacteria can lead to serious respiratory diseases, including asthma, allergic reactions and upper respiratory tract viral infections (i.e. herpes, influenza).
Another source of moisture is the condensation that develops within the barn. Inadequate ventilation, especially from closed doors during cold weather, can lead to increased moisture buildup indoors. The horses themselves are a source of moisture and with the more horses kept in for longer periods, the more condensation that is generated. Therefore, it is vital to refresh the air inside the barn constantly to ensure the health and well-being of the animals.
Natural ventilation offers the most affordable solution with minimal initial investment, zero maintenance expenses, and no energy consumption. However, a combination of natural and mechanical ventilation can enhance air quality and comfort in a stable block.
Installing air inlets low and outlets high in the barn harnesses the natural tendency of warm air to rise, improving ventilation efficiency. To optimise ventilation, high outlet vents should be installed at the roof's ridges, where warm air naturally accumulates.
During winter, the barn doors may remain shut to retain heat, while strategically placed vents ensure adequate airflow, and in summer, windows and stable doors may be left open to promote ventilation and comfort. Using horse body heat to warm a stable leads to very poor interior air quality due to inadequate ventilation and the accumulation of ammonia and other gases. In a well-ventilated, unheated stable with good air quality, the air temperature typically stays within 0-5° C / 5-10° F of the outdoor temperature.
A well-designed mechanically ventilated barn allows for precise regulation of indoor air quality, surpassing the capabilities of a naturally ventilated barn. Power ventilation systems in barns often incorporate exhaust fans and high-volume, low-speed units strategically placed in main aisles, barn ends, or between stables for optimal airflow. Individual fans in stables or aisles primarily serve to disperse particulates and repel insects rather than provide significant cooling.
If you are designing a brand new stable, the steeper the pitch of the roof, the faster the stale air will exhaust through the top ridge vents.
Vents and grates at the bottom of stable partitions help improve air circulation, effectively reducing ammonia fumes from urine. Stabled doors should feature grated panels to ensure both security and proper ventilation.
Water Supply
A steady availability of clean, fresh water is crucial for preventing dehydration and colic. You can provide water in your stable using either buckets or automatic drinking bowls, depending on your setup.
Automatic drinking bowls can be costly and require installation. It's difficult to gauge your horse's water intake, but you can minimise physical labour in the yard and make sure your horse has constant access to fresh, clean water.
Water buckets are an affordable choice and you can track your horse's water intake, but it involves lifting and transporting the buckets to and from the stable.
Lighting
Horses possess an internal timing mechanism known as a circadian rhythm, which regulates various physiological and behavioural functions. This internal clock is controlled by the daily 24-hour cycle of light and darkness and operates in nearly every tissue and organ.
Scientific research supports the use of lighting systems that emit blue light similar to sunlight is advised for daytime use and a soft red light should be utilised during the night. Enhancing stable lighting can optimise the horse's health and wellbeing by supporting its natural circadian rhythm. All elements of their physiology can function more harmoniously and in sync with the environment.
Social interactions
Recent studies indicate that private stables may not promote health and well-being as effectively as communal environments. The results indicated that horses housed in 'parcours' exhibited minimal abnormal behaviours like stereotypies, had the freedom to move throughout most of the day, engaged with other horses, and maintained positive interactions with humans.
Although this may not always be viable within training yards, stable adaptations can be made to increase social interactions. Windows in stables with views to other stables or paddocks allow horses to see and interact, even if they are not in direct contact, stall partitions with bars allow for visual and olfactory contact and individual turnout paddocks or pens allow horses to graze and interact in close proximity.
Feeding and entertainment
Horses should ideally have unrestricted access to hay; however, using slow feeders or automated feeders are also available to provide small portions throughout the day.
Entertainment devices can also help stimulate interaction and engagement, reducing the chances of stress and the emergence of negative habits (vices). Stable toys, mineral licks, stable treats, spreading forage in different locations, visual stimulation such as mirrors and brushes affixed to walls or fences all offer enrichment.
Technology
A range of technology is increasingly accessible to facilitate continuous care around the clock. Technology has the potential to staff, allowing them to redirect their time towards enhancing equine welfare.
The integration of camera-GPS surveillance with specialised software monitors the movements of individuals and determines the typical behaviour patterns for each horse within the herd. This cost-effective technology can alert yard personnel if a horse exhibits unusual behaviour.
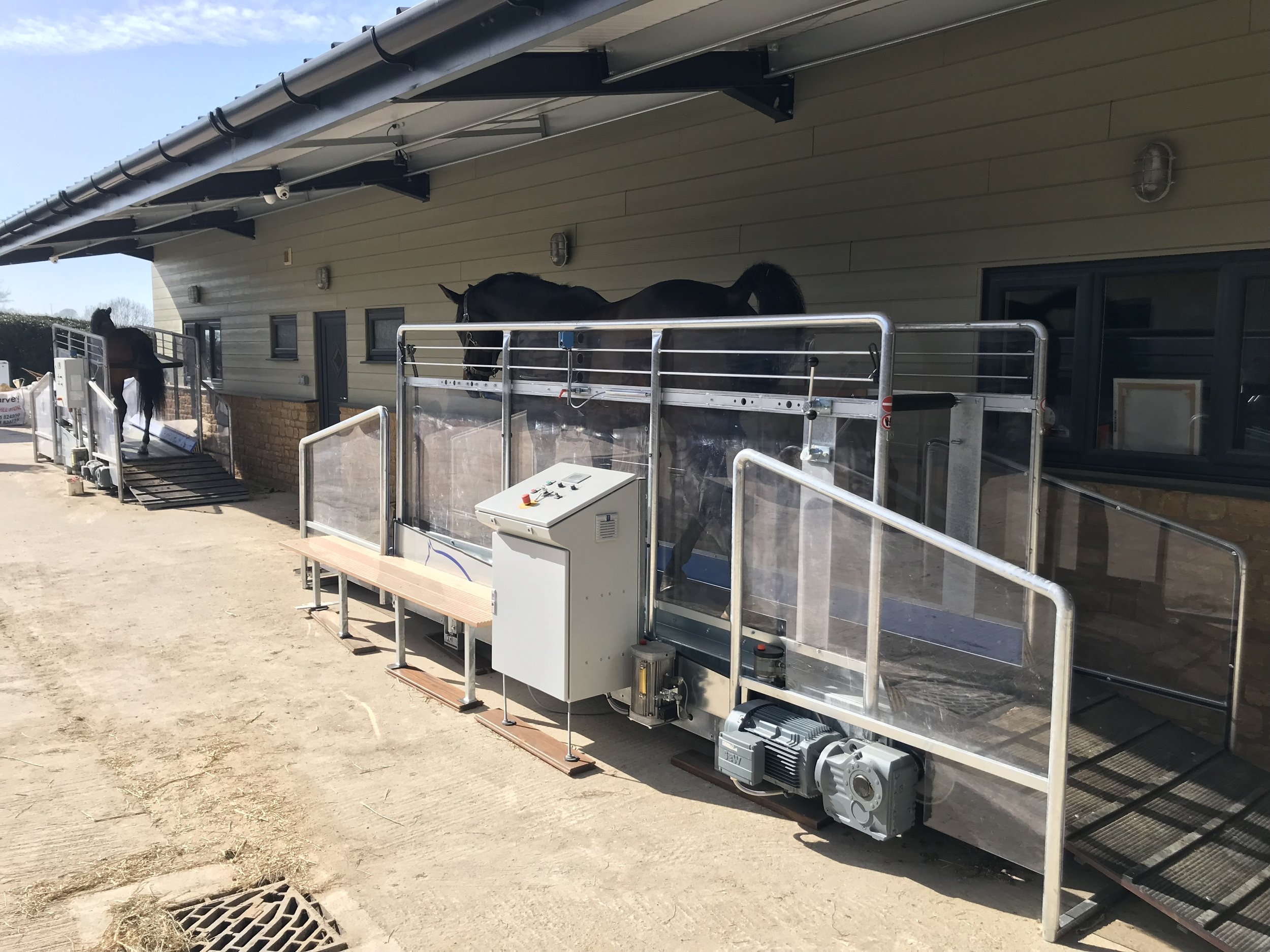
There are a range of therapeutic technologies that can be utilised in the stable environment such as massage rugs, leg wraps and boots and handheld complimentary devices; as well as additional training and rehabilitation systems such as spas, treadmills, combi floors and solariums. All of which can be considered for enhancing the horse's well-being.
Conclusion
Ensuring the comfort and well-being of the horse within the stabled environment by adapting structures and utilising enrichment tools can help prevent injuries, health issues and fire risks. By promoting best practice for keeping the competition horse and ensuring natural behaviours are expressed as much as possible within the training regimes, will only benefit the horse thus increasing performance results.