Irishman Brendan Walsh Strikes Gold in America
/Article by Ken Snyder
The expression “luck of the Irish,” strangely, originated in America from the seemingly uncanny ability of Irish and Irish-American miners to strike it rich in the 19th-century California Gold Rush.
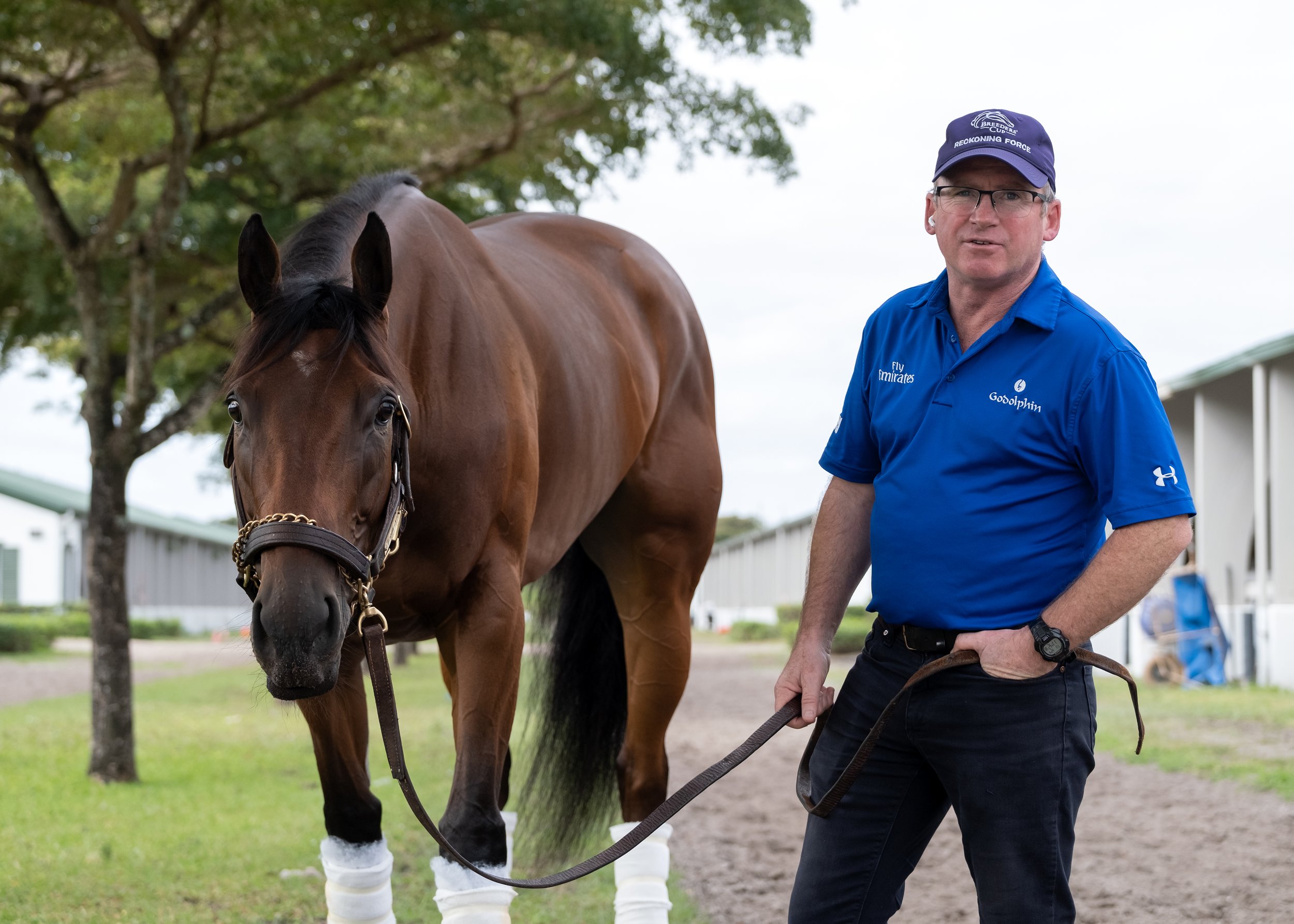
Irish trainer Brendan Walsh from County Cork has also “struck gold” on racetracks throughout America and lots of it. His proteges in 2022 earned $8.3 million after 2021 earnings of $7.5 million. Here’s the real motherlode of surprises about those totals: his previous best year was 2019 when his horses earned a relatively paltry $3.8 million.
The soft-spoken trainer modestly dismisses his personal “gold rush” with a simple and ironic “I got lucky.”
Luck and being Irish had nothing to do with it, of course. The reality with Walsh can be summed up, not in a myth, but in an accepted truth: luck is the residue of hard work.
Walsh’s success began not with a promising two-year-old, a typical route to the stratosphere of trainer earnings, but with a $10,000 claimer. There is maybe some luck there, but keen judgment is the “residue” of hard work. It takes a willingness to closely watch Thoroughbreds— another trainer’s horse or horses. And that’s more than just watching race replays. It’s morning workouts surreptitiously watching a prospective claim, getting good looks at conformation in paddocks and stable areas, poring through past performance for strengths and weaknesses of another trainer with a specific type of horse, knowledge of pedigree, and more, all to find a hidden gem.
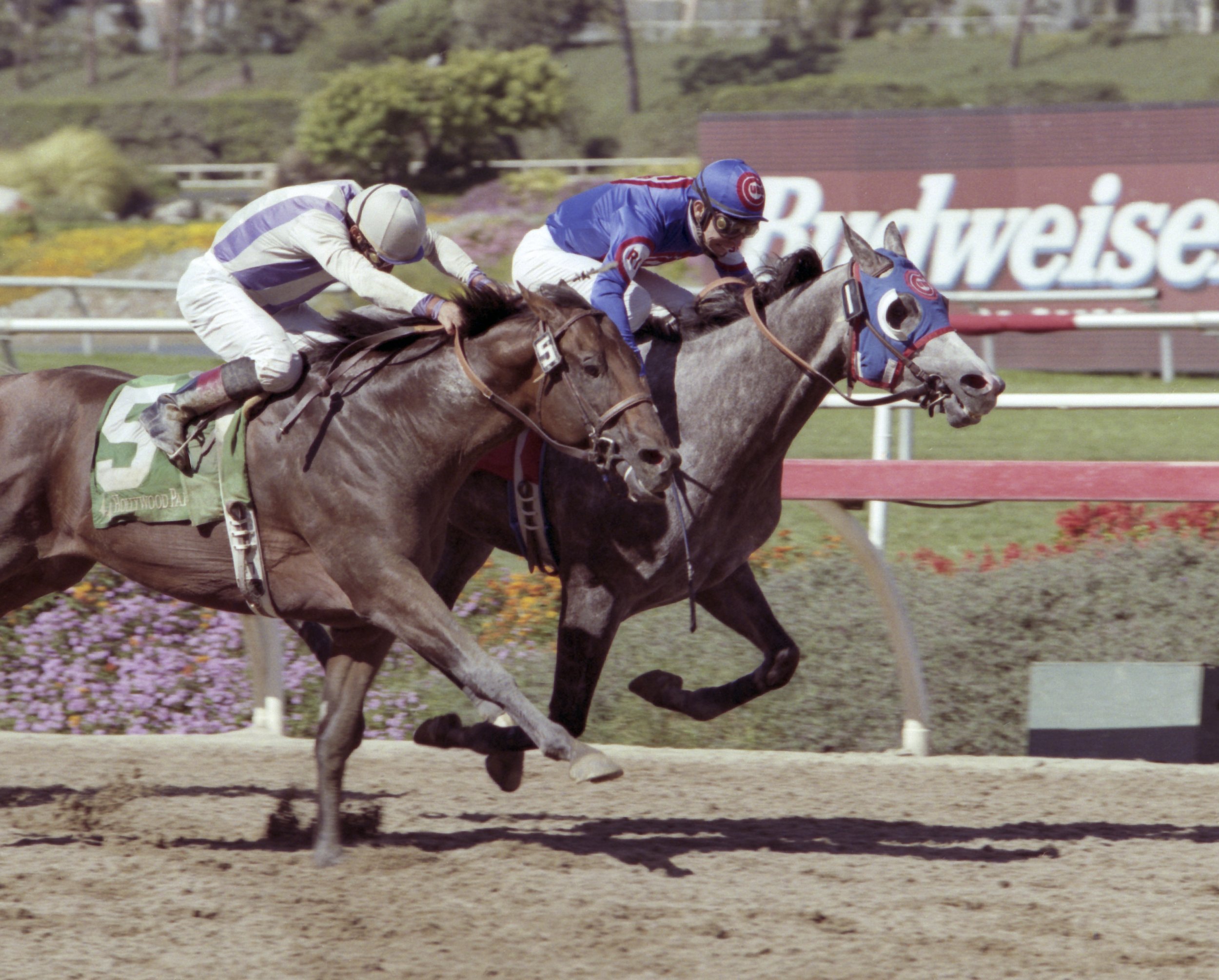
Cary Street was the prize jewel for Walsh. “I owned half of him for most of his career. He paid a lot of bills, won a couple of stakes, and he got me noticed. No matter how many decent horses I’ve trained since, I probably owe more to him than I do any other.”
That a horse running in a $10,000 claiming race could achieve what this one accomplished demanded extraordinary foresight. Walsh believed that a different direction was all the horse needed to realize potential. “I thought he was an out-and-out two-turn horse, and he was sitting on a win. We just worked on him and gave him a lot of time.”
Walsh missed the two-turn prognosis by one turn. In 2014, Cary Street won the Las Vegas Marathon Stakes at Santa Anita, a mile-and-three-quarter Grade 2 race by a whopping nine-length margin…going three turns. Roughly three months earlier, Cary Street won the Greenwood Cup Stakes, a Gr. 3 mile-and-a-half affair at Parx Racing in Philadelphia after only one win in allowance company. Not surprisingly, he was a 28-to-1 long shot.
Both races were stellar performances—the Philly race earning a 107 Equibase speed figure and a 108 in the Las Vegas stakes race.
“If Cary Street hadn’t come along, who knows?” said Walsh with a shrug. “People that don’t make it, a lot of the time it’s not for their lack of ability. You just have to get the breaks.”
“Breaks'' don't account for spotting what turned out to be an extraordinary route runner who earned $381,515 in purses. One factor in Walsh’s success has been exposure to racing globally. Starting at the National Stud in Kildangan in his native Ireland, racing has taken him to Dubai, the Orient, and Arlington Park with Godolphin; and to England and Newmarket where he got his first assistant trainer’s job under Mark Wallace. (Godolphin was to figure prominently later in Walsh’s career.)
His training career in America began when he met countryman and conditioner Eddie Kenneally while on vacation in the U.S. Kenneally invited him to come back at any time to work for him. Walsh took him up on the offer and spent more than three years with him.
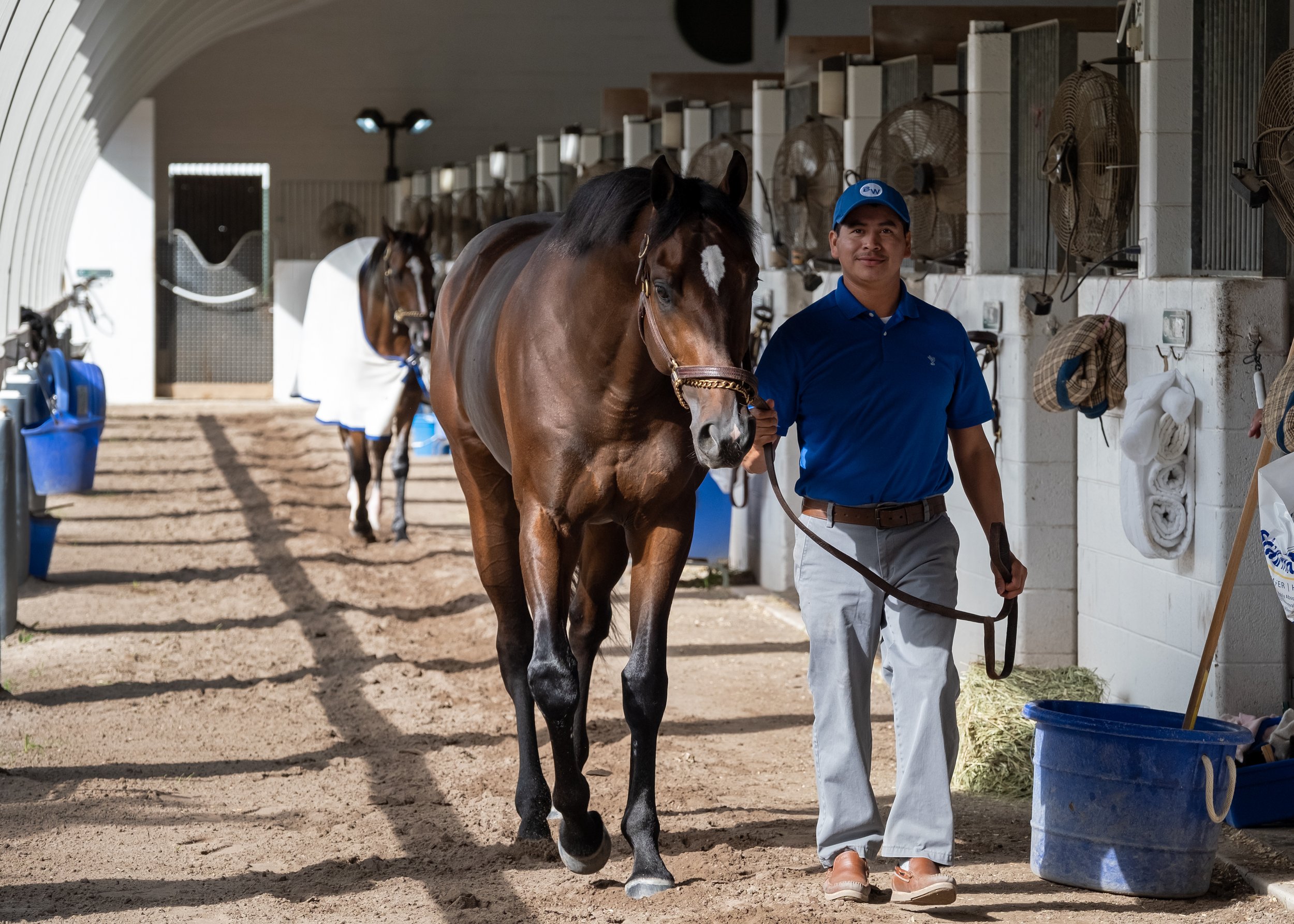
It was at Palm Meadows in Florida where Walsh decided “my time has come. I started with six horses. I had a bridle and saddle. I got six stalls at the track, and away you go,” he said with a laugh.
Not just experience, but the right experience was the best teacher for Walsh. “He [Kenneally] had all kinds of horses—some very good ones—and he dabbled in claiming horses as well. It was a very good education as opposed to going with someone who has a huge barn. You learn about all aspects of training, which was very important to me.”
Oddly, as a native of horse-mad Ireland, American racing always intrigued him. Two summers with Godolphin galloping horses at Arlington Park planted the seed.
“Adjustment-wise, when I came to train in the U.S., it was a whole different ball game. The dirt. The speed. Especially on the dirt, you have to be more aggressive in your preparation, especially young horses starting out, or else you’re going to get buried.
While Ireland is a nation of only 4.9 million, it is surprisingly the largest producer of Thoroughbreds in Europe and third largest behind the U.S. and Australia globally. Another measure of Ireland’s prominence is in Thoroughbred breeding; six out of the current top ten stallions in Europe are Irish-bred, double that of England, the second in the standings for stallions. Despite the wealth of horses, entry into Irish racing is not without obstacles for someone wanting to train, according to Walsh.
“It was very hard for me to have an opportunity to get going in Ireland. There you gotta have a yard. You have to have the backing, and the prize money is not that great.”
The open door with Kenneally opened his eyes to opportunity in this country. “I thought, maybe this is my chance to have a go myself,” he said.
Walsh, who hung his shingle here in the U.S. in 2012, is a repository of insight on both the differences between Irish and American racing and also how similarities have evolved in training methods between the two countries.
Despite repeated success in global events, particularly in the Breeders’ Cup, Walsh believes his countrymen have gone to school on American methods. “When Wesley Ward went over there initially, his horses were hitting the gate so quick and rolling. They were so well prepared. I think it’s actually changed things in Europe a little bit. I think the Europeans may be starting to be a little bit more aggressive with their horses, especially when they have Ascot in mind.”
In Ireland and elsewhere in Europe, many horses no longer get an automatic four-month turnout as has been customary. “That’s changed in Europe now with so many more all-weather tracks,” he said, noting that people are becoming conditioned to year-round racing. “If a horse is sound and he’s doing well, why stop on him for the winter or whatever?”
Still, Ireland has twenty-six racetracks in a country which, in land area, would fit within Texas’ borders twice. Yet, Irish horses won six of the fourteen 2022 Breeders’ Cup races. (U.S.-breds won seven.)
Despite this year’s success of Irish-breds in the Breeders’ Cup and long-standing success with turf races over the years, Walsh sees a change in American horses. “There’s huge improvement with the standard of turf runners compared to ten or twelve years ago. The standard of turf racing in the United States is a lot higher than what it used to be.”
In addition to Ward, Walsh points to trainer Chad Brown as someone producing fantastic turf horses in the last few years. “Bobby Frankel kind of started it,” he added. Brown, perhaps not surprisingly, was an assistant to Frankel before launching out on his own.
As for Irish horses and the Breeders’ Cup, Walsh said, “It’s not a ‘penalty kick’ anymore to bring a horse from Europe,” referencing a high-percentage soccer goal where a single player faces the goalkeeper. In the past,” he added, “a horse bordering on ‘listed class’ in Europe [just below Gp. 1, 2 or 3 races] would win Gr. 2 or 3 races in the U.S.
“It’s not a ‘gimme’ anymore.”
Ireland produces what it does, in part, due to calcium-rich soil much like Kentucky’s—a temperate climate; but perhaps most important, Ireland is a nation where most of the sports focus is on horse racing.
Walsh recalled in his youth that “everybody in Ireland knew somebody who had a horse.” Today, he said, “It’s a little bit like Australia where everybody watches the Grand National. With Cheltenham, everybody has just gone nuts,” said Walsh of the four-day racing festival in southwestern English that pits Irish horses against English-breds and others from continental Europe. “Everybody is in the betting shops during Cheltenham betting on something or other.”
With a smile and probably unable to resist, Walsh observed, regarding Irish versus English horses, “We’ve been wiping the floor with them for a long time.”
Walsh’s exposure to horses came through his father and trips to Cork Racecourse in their home county, engendering in him “from the start” a desire to be a jockey. However, by the time schooling was over, jockeying no longer interested him. Thoroughbred breeding instead became an interest, and he got a spot in Ireland’s National Stud in County Kildare. However, his size and riding background got him started as an exercise rider. “Kildangan used to break and re-train all of Sheikh Mohammed’s and Godolphin Stables’ yearlings and two-year-olds before going on to trainers.”
Walsh was selected in his first year at Kildangan to go to Dubai with Godolphin to gallop the stable’s two-year-old horses. There he got to know Saeed bin Suroor and Tom Albertrani, bin Suroor’s assistant at the time.
“I was lucky enough when I worked for them to travel all over Europe and run horses. I brought horses to Hong Kong, Singapore and Japan. You can’t put a price on that.
“Since Kildangan, you’re probably talking twenty-five years that Godolphin has had an influence on my career.”
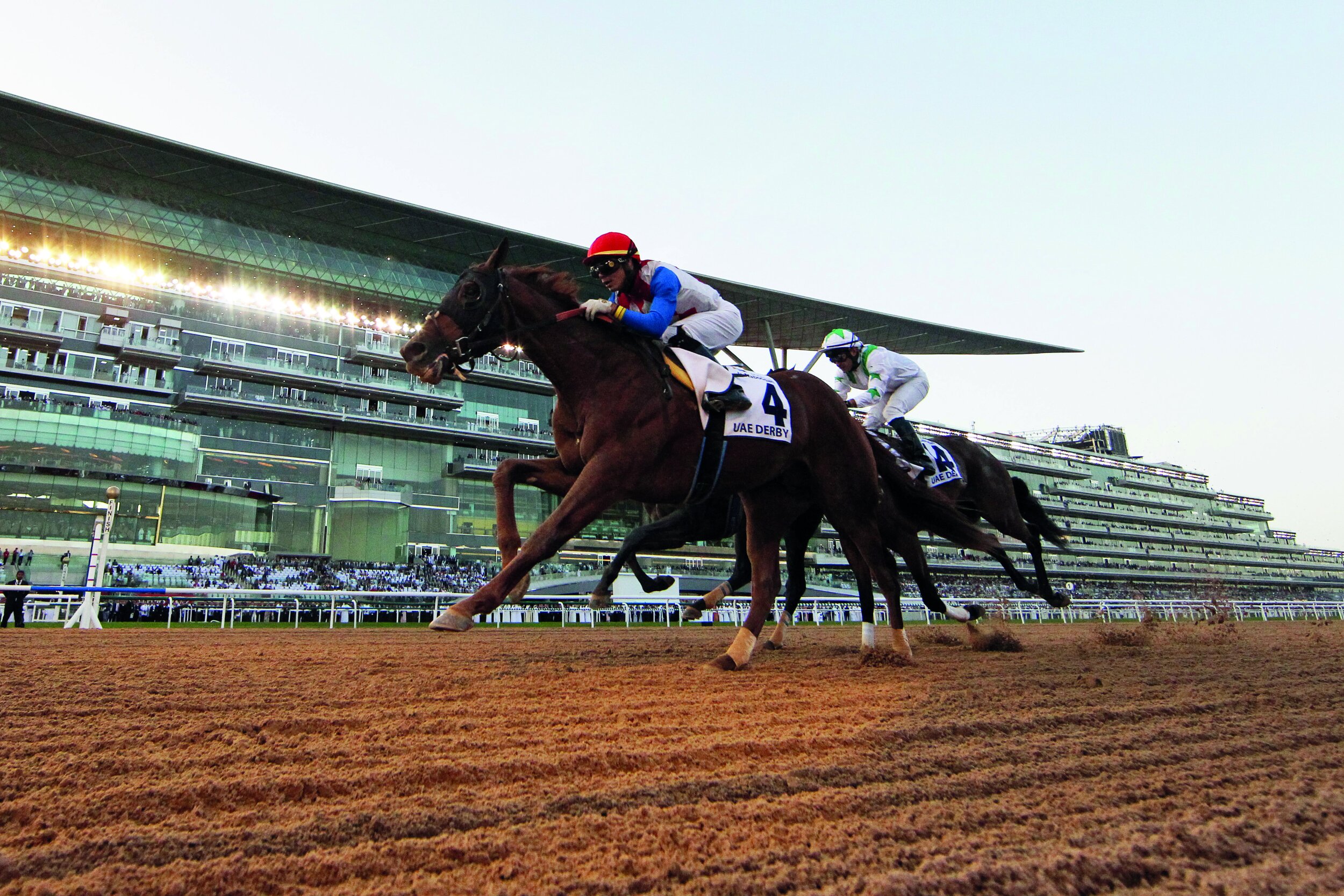
Success with Walsh’s horse Plus Que Parfait in the UAE Derby in 2019 was a career changer attracting the attention of the globally prominent Godolphin stable. “They came along when I came back from Dubai that year.”
Did they ever? Included in the first crop of two-year-olds sent to Walsh was Maxfield, winner of eight out of eleven starts including five Gr. 1 wins and purse earnings topping $2 million. A significant part of ’21 earnings was Maxfield contributing approximately $1.5 million to the bottom line.
As an incredible 2021 has been topped by an even better 2022, a question arises: does he envision getting to the heights of Todd Pletcher, Steve Asmussen, et al. “That would be great. It’s nice to be even thought of as being up to that standard. They’re very good trainers, and they have fantastic horses. A lot of it is the stock and managing it.”
As for managing 200 horses at multiple racetracks around the country like the aforementioned trainers, Walsh is ambivalent. “I don’t know that I would. If you’ve got the team and the owners, you can manage it.” He added: “I’ve got a great team right now.”
Despite the resources to possibly return to Ireland and train there, it is not something that is top of mind. “You do miss certain things.
“The world is a small place. I can get on a plane in Boston and be home in six hours. I come from a family of seven. All of them are in Ireland except one of us--a sister who lives in Jersey [the island in the English Channel and not the state].
“No one else in my family is in racing, but they follow it. They’ve gotten hold of Equibase so they’re keeping up with it pretty good. I go home at least once a year. I don’t stay for too long—five or six days—because I get antsy about what’s going on back here.”
Aside from family, Walsh jokes that other Irish “probably look at me as being an American.”
A win in the Breeders’ Cup—an event followed closely by Ireland’s racing fans (and justifiably so considering 2022 success)—would put him in the spotlight back home, he said.
Santin was a prospect for this year’s event after a win in the 2022 Gr. 1 Arlington Million but was saved for the Clark Handicap after a disappointing finish in his next start in the Coolmore Turf Mile.
Walsh has perhaps become “Americanized” when asked which he would prefer between a win in the Breeders’ Cup or Kentucky Derby. “That’s a hard one to call. When you’re in this country long enough, everybody wants to win the Derby.”
Obviously, the training ability is there with Walsh as well as the trust of racing outfits like Godolphin that can provide him with the best Thoroughbreds.
Luck of the Irish? If there really is such a thing, Walsh won’t need it.